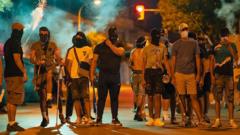In a dramatic turn of events, Spain faced a widespread national blackout due to simultaneous failures in its electricity network. At 12:33 on Monday, the nation lost 15 gigawatts of power, causing widespread disruption across Spain and Portugal. By Tuesday morning, over 99% of power demand was restored, but not without significant effort.
**Spain’s National Blackout: Lessons Learned from a Major Power Crisis**

**Spain’s National Blackout: Lessons Learned from a Major Power Crisis**
After almost 23 hours of chaos, Spain's electricity grid is restored following an unprecedented blackout, prompting urgent discussions on energy reliability and future prevention.
Spain’s power crisis began when two separate outages occurred in the southwest, which were compounded by a disconnection from the French electricity network. This unprecedented loss of power generation raised alarms, particularly as solar power reliance reached a peak just before the collapse. Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez and other public figures speculate that the increased input from renewable sources, especially solar, may have contributed to the system’s instability.
Efforts to restore power focused on hydro-electric plants and combined-cycle gas plants, while the automatic shutdown of several nuclear reactors added to the challenge. Despite the hurdles, neighboring countries like France and Morocco provided vital assistance, transferring much-needed electricity across borders. By the evening of the blackout, Spain's power grid began to stabilize, with important infrastructure like hospitals being prioritized for electricity restoration.
Daily life was thrown into turmoil as transportation systems failed, citizens were left without communication, and various emergency measures were put into place. The economic impact of the blackout could be as high as €1.6 billion, while questions around Spain’s energy policies are being raised. Experts express concern that the inadequate infrastructure may lead to further crises if a balance between renewable energy and grid stability is not achieved.
Amidst all the challenges, the resilience and solidarity displayed by the Spanish population during the crisis were commendable, echoing calls for thorough evaluations to avert future disasters. As Spain navigates the aftermath of this unprecedented event, discussions will intensify on how to fortify its energy systems for a sustainable future.
Efforts to restore power focused on hydro-electric plants and combined-cycle gas plants, while the automatic shutdown of several nuclear reactors added to the challenge. Despite the hurdles, neighboring countries like France and Morocco provided vital assistance, transferring much-needed electricity across borders. By the evening of the blackout, Spain's power grid began to stabilize, with important infrastructure like hospitals being prioritized for electricity restoration.
Daily life was thrown into turmoil as transportation systems failed, citizens were left without communication, and various emergency measures were put into place. The economic impact of the blackout could be as high as €1.6 billion, while questions around Spain’s energy policies are being raised. Experts express concern that the inadequate infrastructure may lead to further crises if a balance between renewable energy and grid stability is not achieved.
Amidst all the challenges, the resilience and solidarity displayed by the Spanish population during the crisis were commendable, echoing calls for thorough evaluations to avert future disasters. As Spain navigates the aftermath of this unprecedented event, discussions will intensify on how to fortify its energy systems for a sustainable future.